- Emily
- December 6, 2016
“In biology, nothing is clear, everything is too complicated,everything is a mess, and just when you think you understand something, you peel off a layer and find deeper complications beneath. Nature is anything but simple.” By Richard Preston. Let this statement not scare you on biology.
Mitosis: In cell biology the process of nuclear division is mitosis. During division the nucleus of the cell separates into two sets of identical chromosomes or organised DNA proteins.
A nucleus is a membrane structure that contains a cell’s hereditary information.
A further process in the cell division called cytokinesis, divides the cells to two totally separate cells called the daughter cells.
The main purpose of mitosis is natural growth of organisms. Worn out, damaged cells are replaced with this process. An example of an animal which uses this process is the lizard. They regrow their tails after they have been cut.
Meiosis: A Greek word meaning small it takes its name from meioun. It is a cellular division but happens in specific type of reproductive cell called gametes. The specialised cell forms reproductive cells such as spores in plants or sperms in human.
In meiosis the DNA from each contributing cell gets mixed up with other little DNA’s from different cells forming parts of the X. The number of chromosomes created in each gamete is reduced from the diploid cell. Chromosomes determine the physical characteristics of a child in the event a pregnancy occurs.
Compare and Contrast Mitosis and Meiosis
| Meiosis | Mitosis | ||
| Type of reproduction | Sexual | Asexual | |
| Genetic | Different | Identical | |
| Definition | Type of cellular reproduction in which number of chromosomes are reduced by half through separation of homologous chromosomes producing two haploid cells | An assexual reproduction process in which the cells divides into two producing a replica, with an equal number of chromosomes in each diploid cell | |
| Crossing over | Mixing of chromosome can occur | Crossing over cannot occur | |
| Number of divisions | 2 | 1 | |
| Occurs in | Human, fungi , plant animals | All organisms | |
| Number of daughter cells produced | 4 Haploid cells | 2 Diploid cells | |
| Paringi of homologs | Yes | No | |
| Chromosome number | Reduced by half | Remains the same | |
| Function | Genetic diversity through sexual reproduction | Cellular reproduction and general growth and repair of the body | |
| Karyokinesis | Occurs in interphase 1 | Occurs in interphase | |
| Cytokinesis | Occurs in telophase 1 and in telophase 2 | Occurs in telophase | |
| Creates | Sex cells only, male sperm cells or female egg cells | Makes every other cell other than sex cells | |
| Centromeres split | Centromeres does not separate during anaphase 1 but during anaphase 2 | Centromere splits during anaphase | |
| Discovered by | Oscar Hertwig | Walther Flemming |
Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis: Has a four stage process. The entire four stage process takes about an hour in duration for the division to complete. The steps follow one another without pause.
Interphase: Chromosomes are dispersed in the nucleus and they appear as chromatin, a network of long thin threads or filaments. The chromosomes replicate to form pairs of identical chromosomes called chromatids. The DNA is synthesised only during interphase stage.
Prophase: The two chromatids remain attached at the centromere. In this phase the spindle begins to form. In animal cells the centrioles separate and become apart radiating asters which are bundle of fibers. Some fibers run from one centriole to another. This are called spindle fibers. In plants the spindles form without the centrioles.
Metaphase: Chromosomes congregate between two ends of which the spindles taper. The equatorial plane is the point where the cell will divide when nuclear division is complete. The chromatids are attached to the spindle fibers at the centromere.
Anaphase: The two chromatids of each chromosome separate at this stage and move to opposite poles. During Telophase new nuclear envelopes form around two groups of daughter chromosomes, and the nucleoli will begin to appear. As the formation of the nuclei is complete the spindle disappears. Cytokinesis which may begin before or after mitosis is completed and finally separates the daughter nuclei to two individual daughter cells.
Importance of Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis is important for sexual reproduction.It allows sexually reproducing organisms to grow and develop from a single cell into a sexually mature individual. This process has allowed
reproduction through generations.
Meiosis maintains the same number of chromosome in the sexually reproducing organism. During crossover important maternal and paternal genes are exchanged. This results in variations of the offsprings. Restriction of multiple number of chromosome and stability of the species is done by meiosis process.
Three Unique Features of Meiosis
Synapsis: This unique feature happens early in during the first nuclear division. The process of producing these complex homologous chromosomes is called synapsis.
Homologous Recombination: Another unique feature is that genetic exchange occurs between the homologous chromosomes. The exchange process is called crossing over.
Reduction Revision: The other feature is that chromosomes do not replicate between the two nuclear divisions. This enables each cell to contain only half of the original complement of chromosomes.(http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/raven6b/graphics/raven06b/other/raven06b_12.pdf)
Meiosis Has an eight stage process.. Single cell division occurs twice during meiosis.
Prophase 1: Crossing over occurs after the chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
Metaphase 1: Pairs of homologous cells chromosomes shift to the equator of the cells.
Anaphase 1: Homologous chromosomes shift to the opposite poles of the cells.
Telophase 1 and Cytokinesis: Chromosomes come together at the poles of the cells and the cytoplasm divides.
Prophase II: A new spindle forms around the chromosomes.
Metaphase II: Chromosomes line up at the equator.
Anaphase II: Centromeres divides. Chromatids gather to the opposite poles of the cells.
Telophase II and Cytokinesis: A nuclear envelopes forms around each set of chromosomes and the cytoplasm divides. (quiznet.com)
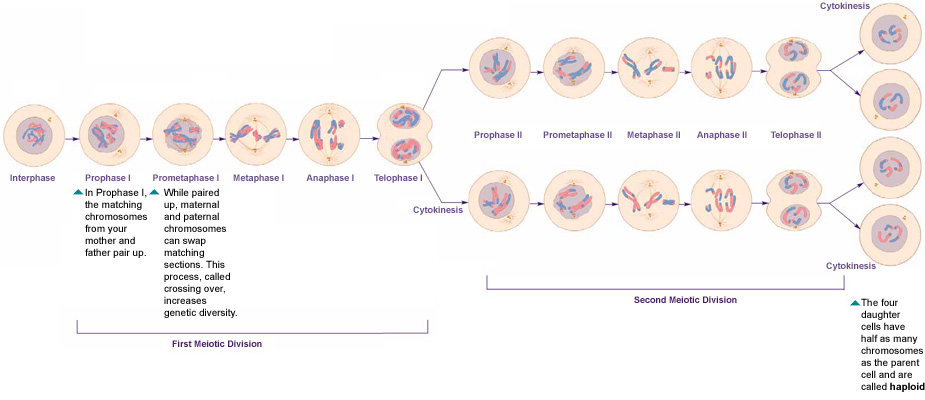
source: https://publications.nigms.nih.gov/insidethecell/ch4_phasesmeiosis_allbig.html
Similarities between Mitosis and Meiosis
Multiple stages: Both are multi stage processes. The same process occurs to each except the difference in chromosome numbers. In both processes sister chromatids are aligned at the metaphase stage. Production of two identical cells to that of the parent cells occurs in the two.
Same Road: The mechanism which pulls the chromosomes apart is the same for both meiosis and mitosis. During metaphase the chromosomes are aligned in the middle of the cells.
DNA Replication: Both involve duplication of a cell’s DNA content. Each strand of DNA is replicated and remains unified. The contrite form of DNA is known as chromosome. Before DNA is detached it must be duplicated then condensed into a form that can be effectively transported.
Rebuilding the Roof: One key similarity is the imperative function of duplication and separation of the DNA content. Separation of chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis must be anticipated by a degradation of the nuclear membrane so that the chromosomes can align in the middle cell and be split equally. (Education.seattlepi.com)
Need a similar research paper or term paper, you can purchase a research paper here
- Comments Off on Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis Research Papers
- Tags: